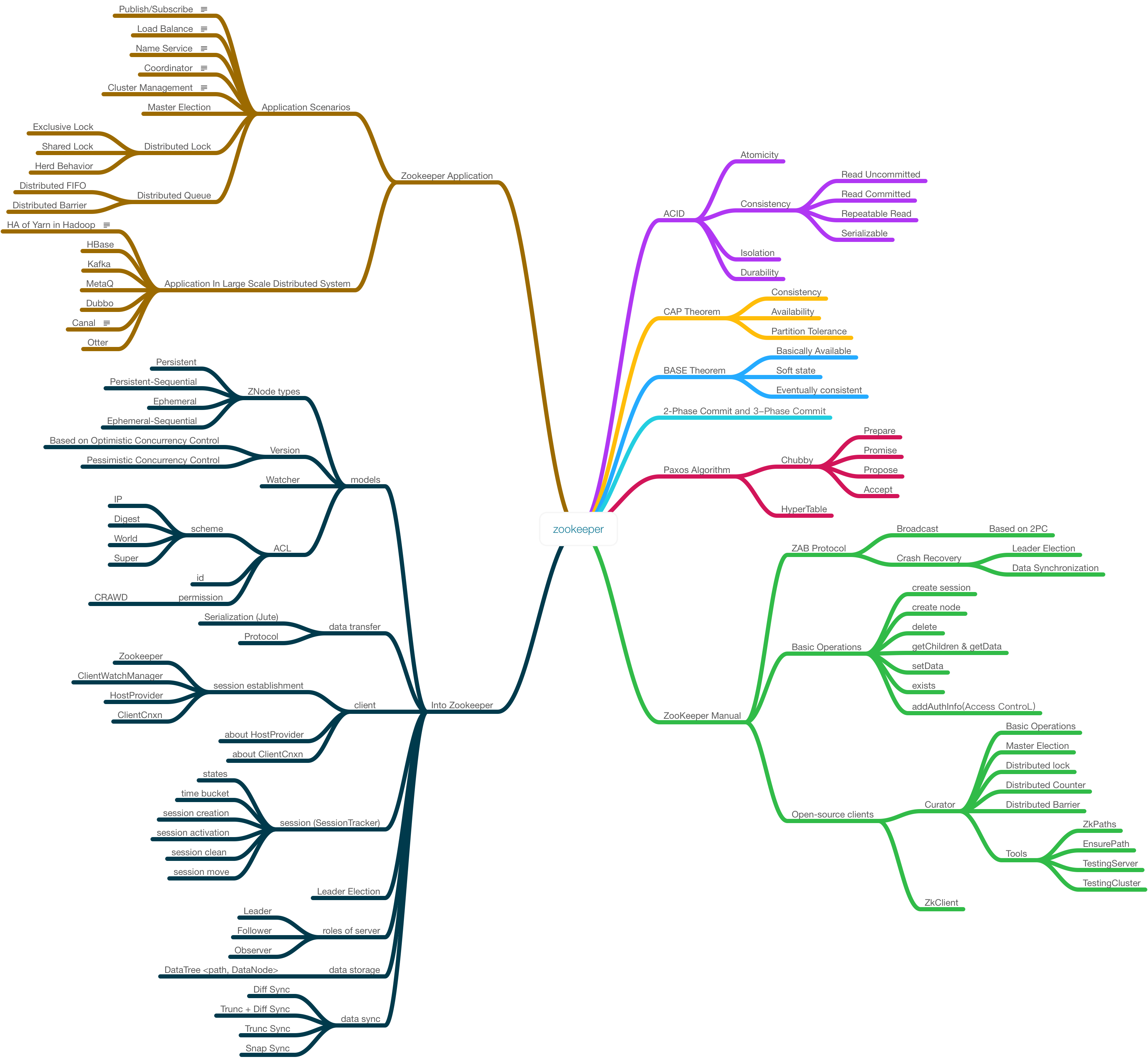
- Knowledge tree
- 1. Basics
- 2. Consistency Protocol
- 3. Zookeeper manual
- 4. Zookeeper Application
- 5. Into Zookeeper
Knowledge tree
1. Basics
1.1 ACID
4 properties of database transactions.
- Atomicity
- Consistency
- Isolation
- Durability
1.2 Isolation Levels
- read uncommitted
- read committed
- repeat read
- serializable
1.3 CAP theorem
It is impossible for a distributed data store to simultaneously provide more than two out of the following three guarantees.
| Consistency | Availability | Partition Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Every read receives the most recent write or an error | Every request receives a (non-error) response – without guarantee that it contains the most recent write | The system continues to operate despite an arbitrary number of messages being dropped (or delayed) by the network between nodes |

1.4 BASE theorem
- Basically Available
- Soft state
- Eventually consistent
2. Consistency Protocol
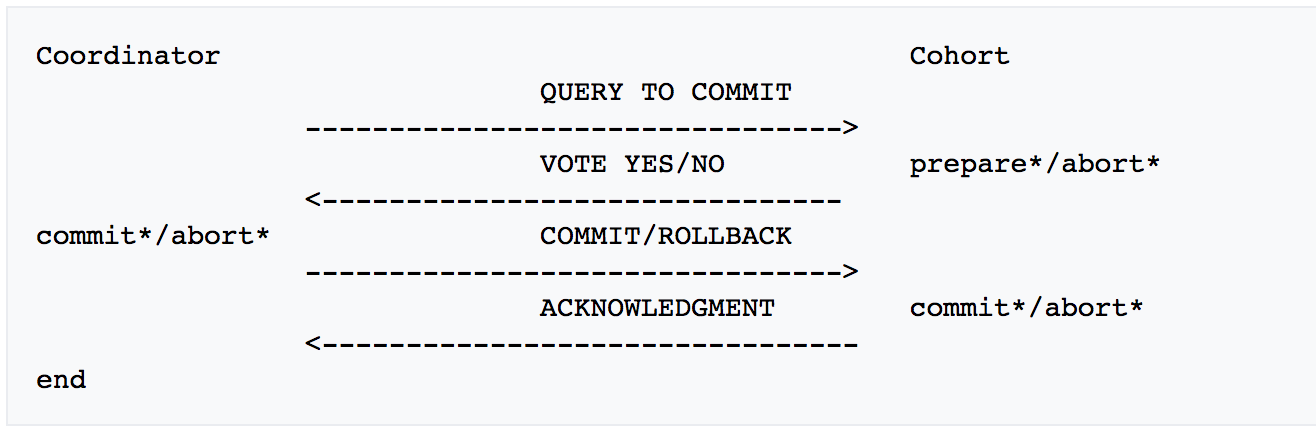
2.1 2PC
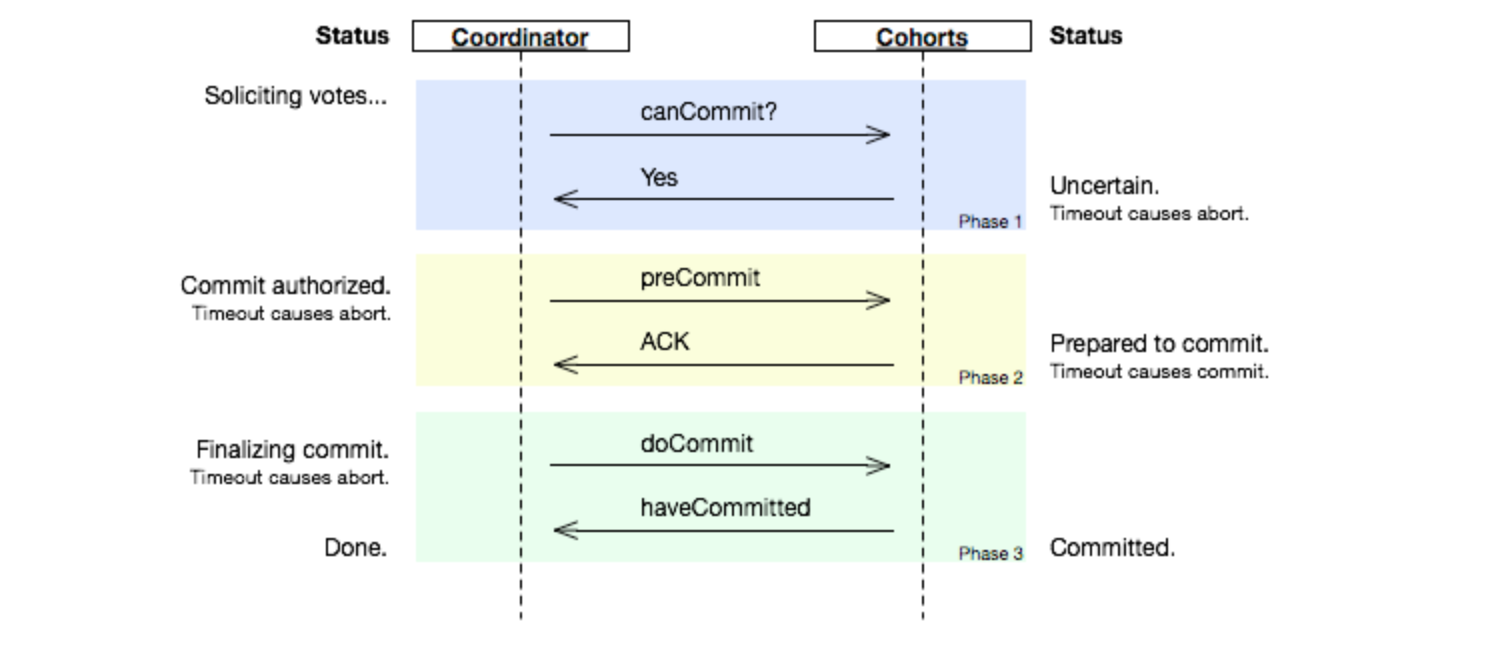
2.2 3PC
2.3 Paxos Algorithm


3. Zookeeper manual
3.1 ZAB protocol
3.1.1 ZAB introduction
-
zookeeper atomic broadcast protocal:

- broadcast based on 2PC
- crash recovery based on Leader Election algorithm and data syncronization strategy (use epoch and ZXID).
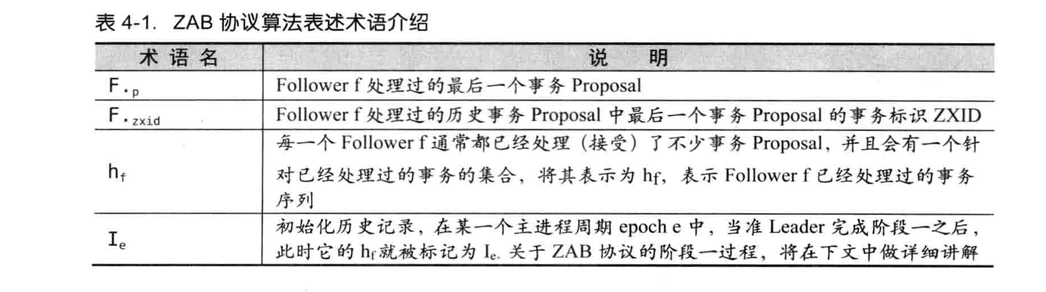
3.1.2 Three phases of ZAB



3.2 Zookeeper Operations
3.2.1 Basic Operations
- new session
- create znode
- delete znode
- getChildren & getData
- znode exists
- auth control addAuthInfo
3.2.2 Opern-source client – Curator
- Watcher: NodeCache & PathChildrenCache
- Master Selection: LeaderSelector
- Distributed Lock: InterProcessMutex & InterProcessLock
- Distributed Counter: DistributedAtomicInteger
- Distributed Barrier: DistributedBarrier & DistributedDoubleBarrier
- Tools: ZkPaths & EnsurePath & TestingServer & TestingCluster
4. Zookeeper Application
4.1 Publish/Subscribe
Config center: every client registers a watcher on the server, when config data contained in the zookeeper node changes, the server sends watch-event to every client, and then clients start to pull new data from server.
4.2 Load balance
Dynamic DNS:
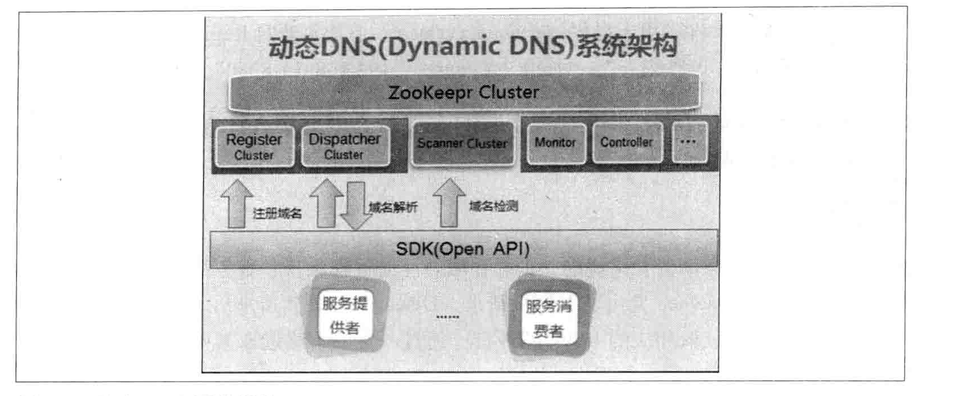
4.3 Name service
Generate GUID: Use znode creation service of zookeeper to generate GUID (Global Unique Identifier).
4.4 Distributed Coordinator
Mysql Replicator: Use zookeeper as a coordinator to manage tasks.
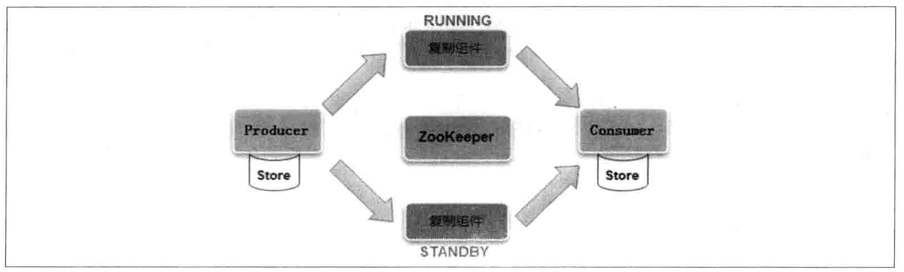
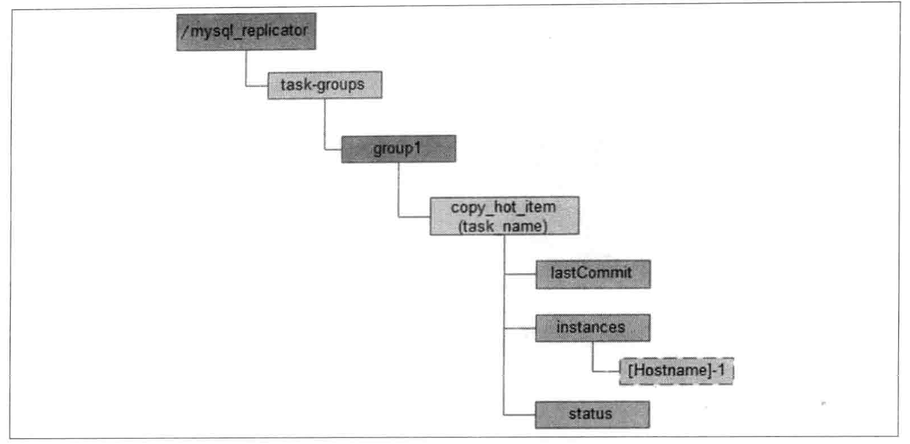
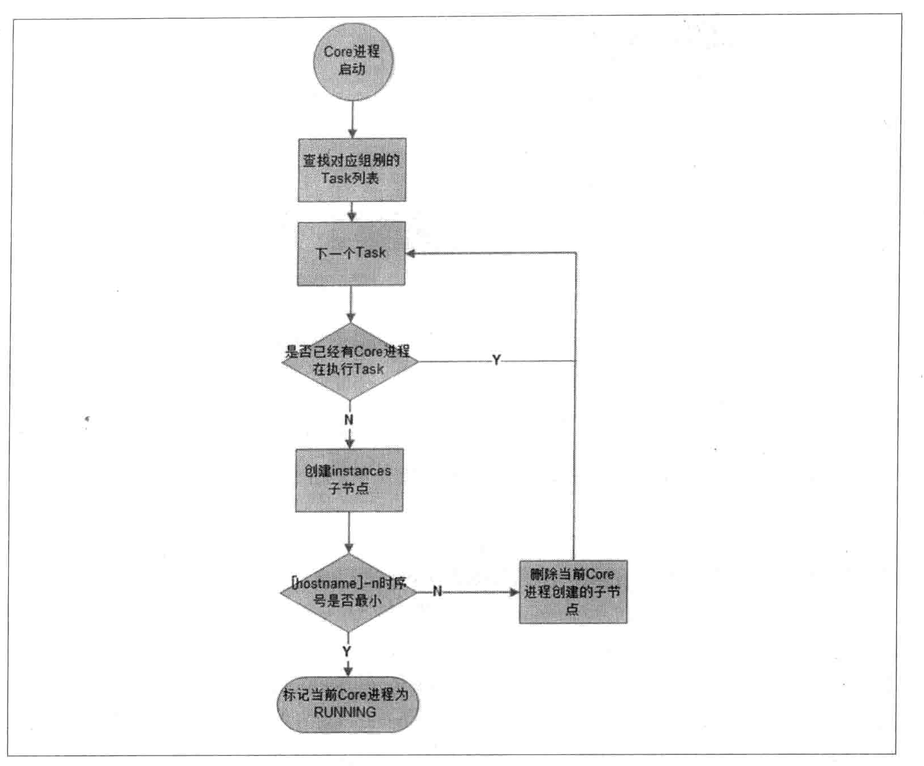
4.5 Cluster management
Distributed Log Collector and Cloud Machine Management
4.6 Master election
Master Election: Use zookeeper’s create-method to elect a master.
4.7 Distributed lock
Exclusive Lock:
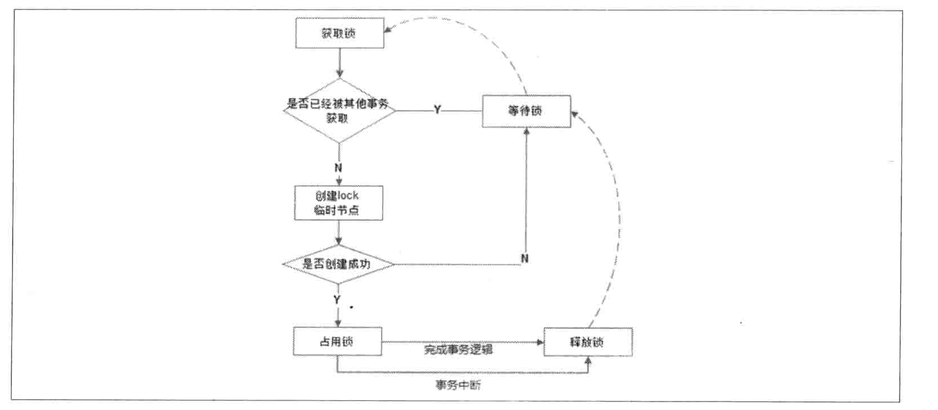 Shared Lock:
Shared Lock:
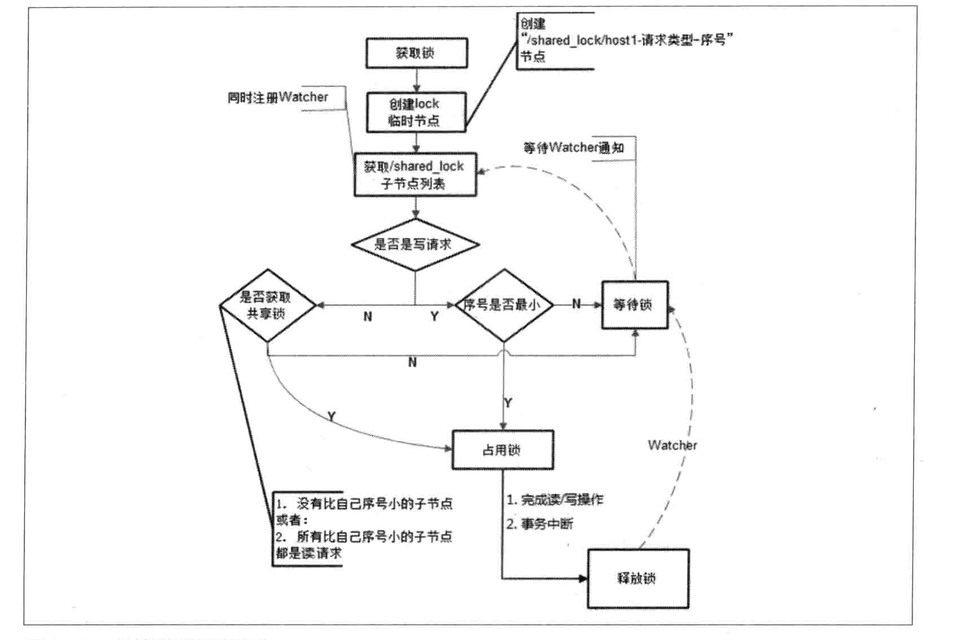

4.8 Distributed queue and distributed barrier
4.9 Distributed Machine Deployment
Machine Deployment: use zookeeper’s Leader/Follower/Observer strategy for machine deployment.
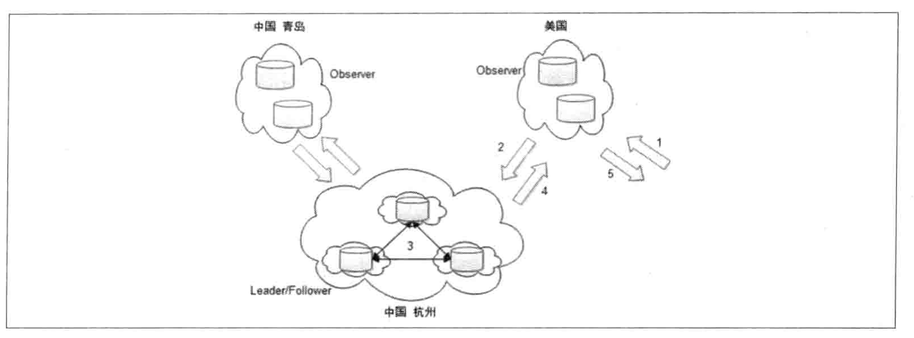
4.9 Attention
Use Fencing to avoid Split-Brain in YARN. For example, Machine-A creates a znode N and is selected as the leader. Then Machine-A gets feign death, that means zookeeper thinks Machine-A is dead. So Machine-B is now selected as the leader and holding the znode N. Then Machine-A recovers from its feign death, and attempts to modify N. To avoid this Brain-Split situation, every znode should be created with ACL info.
5. Into Zookeeper
5.1 Models
5.1.1 znode
- persistent
- persistent-sequential
- ephemeral
- ephemeral-sequential
5.1.2 version
‘version’ for optimistic concurrency control.
5.1.3 watcher
5.1.4 ACL
- scheme: IP, Digest, World, Super
- id
- permission: C R A W D
5.2 Data transfer
5.2.1 Serialization
Jute
5.2.2 Transfer protocol
5.3 Client
Core components:
- Zookeeper instance
- ClientWatchManager
- HostProvider
- ClientCnxn (contains OutgoingQueue and PendingQueue)
- SendThread
- EventThread
Create session steps:
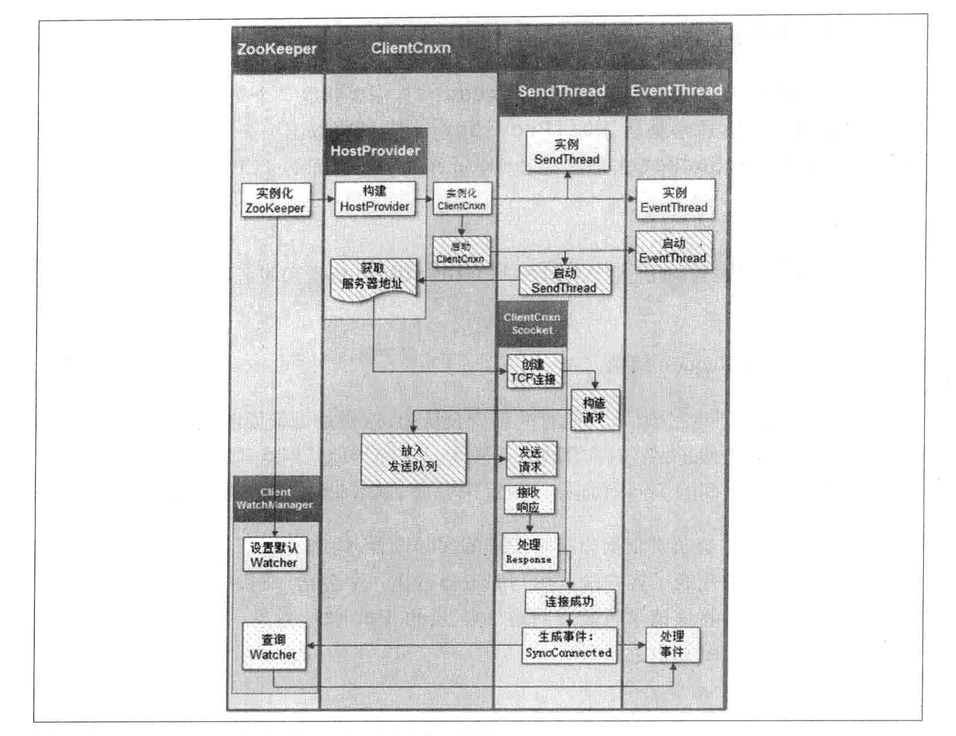
5.4 Session
- states: connected, connecting, reconnected, reconnecting, close
- create session: generate seesionID
- session management: time bucket
- session activation and migration
- session clean
5.5 Leader Election
FastLeaderElection algorithm.

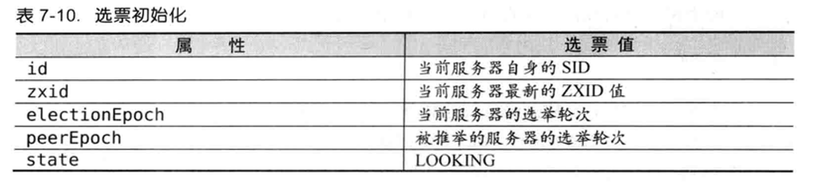



5.6 Data storage
- Memory and ZkDatabase: DataTree<path, DateNode>
- Transactional log
- Snapshot
5.7 Data syncronization
After Learners’ registration to Leader, Learners need to syncronize data from Leader.

- DIFF

- TRUNC + DIFF

- TRUNC
- SNAP
